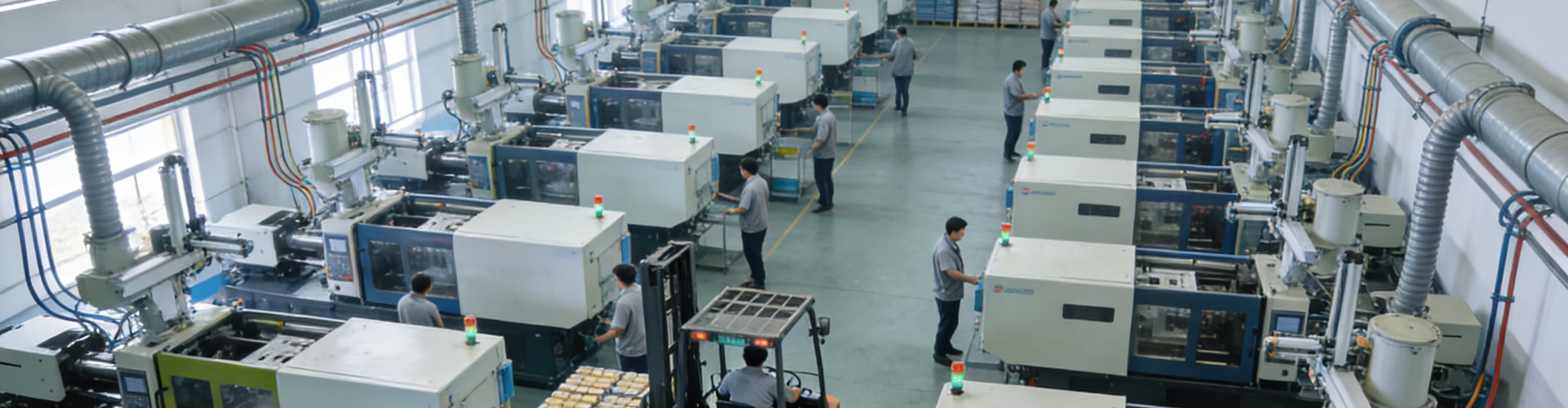
# A Structured Comparison of the Core Information of the Mould Industry in Major Countries The mould manufacturing industry is an extremely important sector, once hailed as the "Mother of Machines" globally. Authorities in China's mould industry opine that "moulds are money-printing machines"; the American industrial community regards the mould industry as the cornerstone of American manufacturing; Germany deems it the emperor of metal processing; Singapore considers it a crucial magnet industry; and many EU countries refer to moulds as gold. Evidently, the mould industry serves as a vital indicator of a country or region's manufacturing prowess. Notably, as early as 1989, China listed moulds as the top priority in the technological transformation sequence of the machinery industry in its industrial policies. ## I. Germany Germany is widely recognized as a powerhouse in mould manufacturing. As one of the earliest countries in Europe to engage in mould production, its mould manufacturing technology and product quality have gained global acclaim, cementing its position as a leading supplier of high-end moulds worldwide. German mould manufacturers share a common conviction: the entire industry must collaborate closely, pool wisdom and efforts, drive technological innovation, learn from each other's strengths, pursue common progress, and leverage collective advantages to achieve success in the sector. To meet the demands of the rapid development of new products today, not only large companies but also numerous small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Germany have established new R&D centers, taking the initiative to conduct research and development for clients. Germany has always attached great importance to research, which constitutes a crucial foundation for its unwavering competitiveness in the global market. Amidst fierce competition, the German mould industry has maintained a strong foothold in the international market for years, with its export rate stably hovering around 33%. According to data from the Verband Deutscher Maschinen- und Anlagenbau (VDMA), Germany is home to approximately 5,000 mould manufacturers. However, the country's mould industry remains dominated by SMEs: 80% of enterprises employ fewer than 20 people, 19% have 20 to 100 employees, and a mere 1% boast a workforce of over 100. Germany has long been at the forefront of global technology, particularly in machinery and manufacturing, equipped with state-of-the-art equipment. Thanks to its early development in the mould industry, its technologies are highly advanced. The per capita annual output value of Germany's mould industry stands at around 2 million RMB. German mould enterprises adhere to a shared code of conduct: "Collaborate closely, pool wisdom and efforts, drive technological innovation, learn from each other's strengths, pursue common progress, leverage collective advantages, and jointly become industry leaders". Such a high level of collaboration is rarely seen in companies across the world, and it serves as a cornerstone of Germany's robust industrial development. Germany is globally renowned for its exquisite processing craftsmanship and production of precision machinery and tools, a characteristic fully embodied in its mould industry. Guided by the consensus that the entire industry must work in unison, tap into development potential, foster an innovative spirit, advance technological progress, complement each other's strengths, and utilize collective advantages to thrive, both large corporations and SMEs in Germany have set up new R&D centers and proactively provide R&D services for clients. Germany has remained highly active in research, which underpins its sustained success in the international market. Statistics from the Tool and Mould Association of the VDMA indicate that the output value of 90 leading German mould enterprises accounts for 90% of the country's total mould output value. ## II. China China's mould manufacturing industry occupies a significant position in the global arena. Nevertheless, due to its relatively late start, there exists a technological gap compared with Western developed countries, especially those possessing core mould technologies worldwide. It is worth noting that China's mould industry ranks alongside those of the United States, Japan, Germany, South Korea, and Italy, essentially sharing the lion's share of the global mould market. However, China's competitiveness stems not from core technologies but from its cost-effective products. In terms of per capita output value of moulds, Japan records 1.2 million RMB, the United States 1.27 million RMB, and Germany 2 million RMB. In other words, the per capita output value of the US and German mould industries is 5 to 9 times that of China's. China is home to approximately 30,000 mould enterprises, among which state-owned enterprises account for 5%, Sino-foreign joint ventures 10%, and the remaining are private enterprises. In terms of employment, conservative estimates suggest that the number of employees in the industry exceeds 1 million. According to an analysis by the Secretary-General of the International Association of Mould, Hardware and Plastic Industry Suppliers, the development trends of China's mould industry over the next decade will be as follows: mould products will evolve towards larger sizes, higher precision, greater complexity, cost-effectiveness, and faster production cycles; the technological content of moulds will continuously increase while the manufacturing cycle will be shortened; mould production will move towards informatization, paperless operations, precision, and automation; and mould enterprises will develop in the direction of technological integration, sophisticated equipment, brand building, information-based management, and internationalized operations. As we all know, moulds are the "Mother of Machines", and automotive moulds are the "forerunners" in automobile manufacturing. Automotive moulds can be categorized into five major types by function, including stamping moulds and injection moulds. As a type of cold stamping mould, large-scale automotive body panel moulds are the most iconic process equipment products in the automotive mould sector. Due to the complex manufacturing process technology, high requirements for dimensional and surface precision, and the need for high-precision CNC equipment such as five-axis high-speed machining centers, the manufacturing technology of large-scale external automotive body panel moulds has long been dominated by multinational specialized companies. It is worth mentioning that over the past decade, China's mould manufacturing technology has achieved a qualitative leap. The mould industry has grown from a small scale to emerge as a global manufacturing powerhouse. Especially with the development of China's automotive industry, the advancement of independent brands towards the mid-to-high end, and the rise of new energy vehicles, the market has put forward new demands. These demands require China to upgrade from low-end moulds to high-end ones, transform from a major mould manufacturing country into a strong one, and realize the second take-off of China's mould industry. Notably, the six major mould manufacturing countries—China, the United States, Japan, Germany, South Korea, and Italy—account for an absolute dominant position in the global mould output value, with China boasting the highest mould output value in the world. The China Mould & Die Industry Association has conducted a comparative analysis of 20 major global mould manufacturing countries from the dimensions of market size, competitiveness, and development potential. These 20 countries are divided into four groups: "All-Stars" (Germany, Japan, South Korea, the United States, China), "Famous Names" (Switzerland, Canada, Austria, Italy, Spain), "Rising Stars" (Portugal, Czech Republic, Poland, Turkey), and "Novices" (Mexico, South Africa, India, Brazil, Indonesia, Vietnam). China's mould design and manufacturing capabilities have witnessed rapid improvement. In particular, new technologies such as computer-aided technologies including CAD/CAE/CAM, high-speed machining technology, hot runner technology, gas-assisted injection molding technology, and reverse engineering have been widely applied. Technologies such as composite material stamping mould technology, two-component integrated injection mould technology, and high-gloss mould technology have also been put into use. China's status as a major mould manufacturing country has been widely recognized worldwide. China is capable of producing multi-station progressive dies with a precision of 2 microns and a service life of over 300 million strokes. Individual enterprises can manufacture multi-station progressive dies suitable for high-speed stamping presses operating at 2,000 strokes per minute, with a precision of up to 1 micron. In the field of large-scale plastic moulds, China can produce plastic shell moulds for 43-inch large-screen color TVs and 65-inch rear-projection TVs, complete sets of plastic part moulds for 10kg large-capacity washing machines, as well as plastic moulds for automotive bumpers and integral instrument panels. In terms of precision plastic moulds, China has the capacity to manufacture plastic part moulds for cameras and mobile phones, multi-cavity small-module gear moulds, and 7,800-cavity plastic packaging moulds with a precision of 5 microns. Regarding large-scale, precision, and complex die-casting moulds, domestic manufacturers can produce die-casting moulds for integral escalator pedals, die-casting moulds for automotive rear axle gearboxes, and casting moulds for automotive engine casings. In the area of automotive panel moulds, China can now produce panel moulds for mid-range new model cars. China's radial tire segment moulds, aluminum alloy and plastic door and window profile extrusion moulds, and stretch forming dies manufactured via precision casting or resin rapid prototyping have also reached a relatively high level, and the produced moulds are comparable to imported ones. ## III. Japan Japan's mould production capacity once accounted for approximately 40% of the global total, ranking first in the world, and it exports a large number of moulds to foreign countries every year. Japan's top five mould importing countries and their respective import shares are as follows: South Korea (59.8%), mainland China (18.4%), Thailand (4.3%), and the United States (2.8%). Japan is home to world-renowned large-scale cemented carbide tool manufacturers such as Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd., Toshiba Tungaloy, Dijet, Hitachi Tools, Japan Tungsten Industry Co., Ltd., and Fuji Mould. In addition, Japanese mould manufacturers attach great importance to polishing and grinding processes in terms of technology, while German mould manufacturers focus on improving the precision and efficiency of machining and electrical discharge machining to reduce the time spent on manual processing. It is worth noting that Japan not only controls the core technologies of global moulds in many fields but also grasps the most profitable links in the industrial chain, leaving only the profits from the assembly link for most joint ventures in other global markets. In fact, Japan's economic model of "industrial nation-building" is worthy of learning. Notably, Japan has proposed six main development directions for the mould industry: adopting high and new technologies as much as possible to enhance the level of digitalization and informatization; developing new application fields for moulds, such as various new energy, new materials, medical, and aerospace fields; extending the mould industrial chain; carrying out diversified operations; updating knowledge; and promoting development and the integration of industry, universities, and research institutions. At the government level, Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has organized the "Strategic Study Committee on Blank Material Technology" and issued the *Blank Material Technology Strategy* as a guideline. The goal of implementing this technological strategy is clear: "to grasp the lifeline of global manufacturing by mastering key blank material technologies". Japan has approximately 10,000 mould enterprises. In terms of the number of employees, about 91% of enterprises have fewer than 20 employees, and the remaining 9% have more than 20 employees. This figure is quite striking, indicating that the scale of Japan's mould enterprises is generally small. Their main advantage lies in concentration and single product supporting cooperation. Taking automobiles as an example, a complete car requires about 8,000 stamping parts, and each mould factory is assigned to produce several fixed parts. This achieves "precision and centralized specialization" to reduce costs. The per capita annual output value of Japan's mould industry is approximately 1.2 million RMB. With the rapid rise of the mould industries in China and South Korea, which have exerted a significant impact on Japan with their price advantages, especially in the low-to-medium-end mould market with low technical content, they have become major competitors of Japan's small and medium-sized mould enterprises. Therefore, Japanese mould enterprises have begun to focus on the production of high-end moulds and technological upgrading to avoid price competition. That is to say, they take the technological accumulation of "small but refined, small but specialized" as the source of competitiveness, prompting small and medium-sized mould enterprises to continuously innovate and create an environment for sustainable development. Many Japanese mould manufacturers are actively expanding equipment investment. In terms of processing, they extensively adopt unattended processing units or conduct online control through computers. The technological development of moulds mainly proceeds towards high precision, high speed, long service life, complexity, large size, integration, and high performance. ## IV. The United States The United States is a global powerhouse in mould manufacturing, ranking among the first tier in the world's mould industry. Currently, there are approximately 8,000 mould enterprises in the United States, of which 60% employ fewer than 15 people, and 30% have 15 to 50 employees. Due to the highly developed industrialization, the US mould industry has long been a mature high-tech industry, thus occupying a leading position in the world. It is worth noting that the US mould industry features a very clear division of specialized labor, with each mould factory having its own prominent advantageous products and basically focusing on a single niche. For example, Synergis Technologies, a US-based mould factory, specializes in manufacturing chassis subframe moulds, progressive dies, and multi-station moulds. According to surveys, there are about 8,000 mould enterprises in the United States, and more than 90% of them are small enterprises with fewer than 50 employees. In terms of the number of employees, 60% of enterprises have fewer than 15 people, 30% have 15 to 50 people, and the remaining 10% are large-scale enterprises. Despite their small size, these enterprises are equipped with advanced equipment, sound management mechanisms, and automated production systems. Surveys show that the per capita output value of the US mould industry exceeds 1.5 million RMB. Notably, the production and supply of mould steel in the United States have been standardized. CAD/CAE/CAM technologies are widely used in mould design and manufacturing. Advanced equipment is deployed for processing technology and inspection and testing. The development of large-scale, complex, precision, long-life, and high-performance moulds has reached the global advanced level. The US mould manufacturing industry has the following characteristics in production and operation: 1. **Streamlined Staffing**: Most US mould enterprises are small in scale, with few having more than 100 employees. The number of employees in mould enterprises generally ranges from 20 to 50. The staffing of various departments within enterprises is extremely streamlined, with employees being multi-skilled and taking on multiple roles. There are virtually no redundant staff in these enterprises. 2. **Product Specialization and Precise Positioning**: Most US mould factories determine their product positioning and market positioning based on the demand for various types of moulds from industries such as automotive and electronics. To survive and develop in the market competition, each mould manufacturer has its own unique advantageous technologies and products and adopts specialized production methods. 3. **Advanced Management Information Systems and Integrated Management**: Mould enterprises in the United States, especially large-scale ones, have basically achieved computerized management. Computers are widely used in production planning, process formulation, quality inspection, inventory management, statistics, and other aspects. All departments within the company can share information through computer networks. 4. **Advanced Process Management and High Standardization**: US mould manufacturers ensure the precision of parts and production schedules by virtue of advanced process equipment and process routes. The advanced technologies and management practices of European and American mould enterprises have enabled them to produce large-scale, precision, and complex moulds, which have played an extremely important role in promoting the development of industries such as automotive, electronics, communications, and home appliances. For instance, the Ford Motor Company's mould factory in the United States can produce side panel moulds in only 8 weeks, a feat that many consider a miracle, yet the Americans have accomplished it. The preliminary process and design of the moulds are not undertaken by the mould factory but by the R&D department. The mould factory is only responsible for the manufacturing process starting from the foam model. Thanks to the thorough preliminary work, there are few modifications during processing, which saves a great deal of time in mould manufacturing. The mould factory processes foam models for casting. Once the castings are returned, CNC machining commences. With multi-workbench automatic switching, the machines operate 24 hours a day, resulting in high processing efficiency. Moreover, due to the detailed consideration of factors such as springback and deformation in the preliminary work, coupled with precision calculation technology, the processed moulds can be directly installed on the press for debugging, with the first-pass yield rate reaching 85-90%. This demonstrates the extremely high level of specialized processing technology in the United States. ## V. Italy The production technology level of Italian mould enterprises ranks among the top tier internationally. According to the Executive Secretary-General of China's International Association of Mould, Hardware and Plastic Industry Suppliers, the application of high and new technologies in mould design and manufacturing has become a powerful guarantee for Italy to rapidly produce high-quality moulds. Notably, technologies such as CAD/CAE/CAM, high-speed cutting technology, rapid prototyping technology, and rapid tooling technology have been widely adopted in Italian mould enterprises. The key details are as follows: 1. **Widespread Application of CAD/CAE/CAM**: It demonstrates the advantages of using information technology to drive and upgrade the mould industry. In terms of CAD application, Italian enterprises have moved beyond the initial stage of discarding drawing boards and 2D drafting, and currently, 3D design accounts for 70% to 89%. Software such as PRO/E, UG, and CIMATRON are widely used. The application of these software not only enables 2D design but also generates 3D models, providing a guarantee for NC programming and CAD/CAM integration. 3D design also allows for assembly interference checks during the design phase, ensuring the rationality of the design and process. The widespread use of CNC machine tools guarantees the processing precision and quality of mould parts. For example, a mould enterprise with 30 to 50 employees generally owns more than 10 CNC machine tools. Parts processed by CNC machine tools can be directly assembled, significantly reducing the number of assembly fitters required. CAE technology is very mature in Italy. Especially in injection mould design, CAE analysis software is used to simulate the plastic injection molding process, analyze the cooling process, and predict potential defects during the molding process. In stamping mould design, CAE software is applied to simulate the metal deformation process, analyze the distribution of stress and strain, and predict defects such as cracking, wrinkling, and springback. The role of CAE technology in mould design is becoming increasingly important. After applying CAE technology, Italy's COMAU company has reduced the trial mould time by more than 50%. 2. **High-Speed Cutting Technology for Shortening Mould Manufacturing Cycles**: To shorten the mould manufacturing cycle and enhance market competitiveness, Italian mould enterprises generally adopt high-speed cutting technology. High-speed cutting is a processing technology characterized by high cutting speed, high feed rate, and high processing quality. Its processing efficiency is several times, or even more than ten times, higher than that of traditional cutting processes. Notably, Italian mould enterprises extensively use CNC high-speed milling machines in production, including 3-axis linkage and even 5-axis linkage models, with spindle speeds generally ranging from 15,000 to 30,000 r/min. The adoption of high-speed milling technology can greatly shorten the mould manufacturing time. The mould surfaces after finish machining by high-speed milling only require slight polishing before use, saving a significant amount of time for grinding and polishing. Italian mould enterprises attach great importance to technological progress and equipment renewal, with the equipment depreciation period generally ranging from 4 to 5 years. Adding CNC high-speed milling machines is one of the key focuses of equipment investment for mould enterprises. 3. **Popularization of Rapid Prototyping and Rapid Tooling Technologies**: Due to the increasingly fierce market competition and the accelerating pace of product upgrading, rapid prototyping and rapid tooling technologies have emerged and been rapidly and widely applied. It is worth mentioning that Italy's plastic and rubber processing machinery and mould manufacturing industry was once one of the 10 specialized machinery manufacturing industries under the Italian Federation of Mechanical Engineering Industries. Importantly, it has owned more than 500 European patents, boasting a high degree of specialization, advanced technology, a diverse range of products, and the provision of various value-added services to clients. According to reports, the per capita annual sales volume of Italian mould enterprises exceeds 100,000 US dollars. The output value of Italy's plastic and rubber processing machinery and mould manufacturing industry accounts for 16.5% of the total output value of the 10 industries under the Federation of Mechanical Engineering Industries. With their advanced technologies and management practices, Italian mould enterprises produce large-scale, precision, and complex moulds, which play an extremely important role in promoting the development of industries such as automotive, electronics, communications, and home appliances. ## VI. South Korea South Korea is an economic powerhouse driven by high technology. Since the 1970s, South Korea has experienced sustained and rapid economic growth, with its per capita gross national product increasing from 87 US dollars in 1962 to 10,548 US dollars in 1996, creating the "Miracle on the Han River". It joined the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 1996 and became one of the founding members of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in the same year. The output of South Korea's shipbuilding, automotive, electronics, steel, and textile industries ranks among the top 10 in the world. Its semiconductor sales volume ranks first globally, and its crude steel output ranks sixth. Products such as memory chips, liquid crystal displays (LCDs), plasma display panels (PDPs), and mobile phones hold leading positions in the global market. The number of industrial robots in operation ranks third in the world. As early as 2013, the number of industrial robots manufactured in South Korea ranked fourth globally. Since 2014, South Korea has launched the "Manufacturing Innovation 3.0" strategy, vigorously developing 13 emerging growth industries such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), intelligent automobiles, robots, intelligent wearable devices, and intelligent medical care. South Korea aims to build 10,000 smart manufacturing factories by 2020, transforming one-third of the country's factories with more than 20 employees into smart factories. According to the South Korean government's forecast, through the implementation of the "Manufacturing Innovation 3.0" strategy, the export volume of South Korea's manufacturing industry is expected to reach 1 trillion US dollars by 2024, and its manufacturing competitiveness will enter the top 4 globally. South Korea's mould processing industry ranks among the first tier in the global mould sector, with almost every factory being a specialized enterprise. Notably, South Korea attaches great importance to the introduction and application of new technologies. The output value of South Korea's mould industry reached approximately 100 billion US dollars in 2012, close to that of Japan, with one-fourth of its moulds exported to countries and regions such as Japan, China, and the United States. It is worth noting that the future development trend of South Korea's world-leading motorcycle mould processing industry is a paperless and networked processing model. Mould development has transitioned from profile copying processing to fully numerical control processing. For example, software such as PRO/ENGINEER is used for 3D solid modeling, mould design, and CNC programming, making the rapid and high-quality development of moulds a reality. ## VII. Singapore Singapore is a small country with a population of only 3 million. The Singaporean government attaches great importance to and supports the development of precision moulds, introducing many important policies aimed at enabling the rapid growth of the mould industry to boost the country's economic development. Singapore is home to more than 1,000 enterprises engaged in various types of moulds and precision processing, with the annual output value of the mould industry once exceeding 4.5 billion RMB. Singapore's mould processing industry holds considerable influence and plays an important role in the Asian mould industry. Notably, more than 10 of Singapore's mould enterprises are listed companies. Over 65% of the moulds produced by enterprises in Singapore are supporting products for the IT and electronics industries. Although the moulds produced are not large in size, they are all high-precision and high-level products. Singapore's mould enterprises mainly focus on fields such as semiconductor frame/packaging moulds, metal stamping moulds, plastic moulds, and silicone rubber moulds. ## VIII. Switzerland Switzerland has a land area of only 41,000 square kilometers and a population of 8.5 million (as of 2018), yet its economic aggregate ranks among the world's largest. Switzerland is home to 21 Fortune Global 500 companies (as of 2019), spanning sectors such as finance, pharmaceuticals, retail, and industrial manufacturing. "Swiss-made" represents brand and quality, embodying not only precision technology but also meeting aesthetic demands. From world-famous Swiss watches and Swiss Army knives to precision instruments, accuracy is a defining characteristic of these products. In comparison with German manufacturing, the Swiss often joke that Swiss products are slightly more expensive than German ones but also slightly more precise, which reflects the unique advantages of Swiss manufacturing. Since 1901, Switzerland has produced 24 Nobel laureates. Calculated based on the total population, Switzerland has the highest number of Nobel laureates per capita in the world. The renowned Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH Zurich), the alma mater of Albert Einstein, has nurtured 32 Nobel laureates. Switzerland attaches great importance to innovation, ranking first in the Global Innovation Index for 8 consecutive years among the world's top 20 innovative economies. On average, there are 11.2 researchers per 1,000 people in Switzerland, and the country's R&D expenditure accounts for approximately 2.9% of its GDP. On December 11, 2019, the 2019 "World's 500 Most Influential Brands" ranking compiled by the World Brand Lab was announced in New York, USA. A total of 29 countries were represented in the ranking, with Switzerland having 21 brands selected. Switzerland's electromechanical and metal industry is the mainstay of its industrial sector. The output of products such as textile machinery, printing equipment, packaging machinery, precision tools, and turbines ranks among the top in the world. After 25 years of operation, Switzerland's mould industry has developed into one of the most important mould manufacturing sectors in the country. For example, Switzerland's Area Company specializes in the manufacturing of die-casting moulds and plastic part moulds. In terms of injection molding technology, it has developed the AWM hot runner injection system. The moulds produced by the company are mainly used for manufacturing cassette cases, such as those for music, video, movies, and color tapes, as well as other high-precision parts produced in large quantities, such as connectors used in the electronics industry. More than 90% of its products are exported to countries around the world. It is worth noting that Switzerland's mould production technology is of a high level, featuring high surface finish of parts, small clamping gaps, and the widespread use of hydraulic core-pulling in large-scale die-casting moulds. The production efficiency is high, with an average of 5 to 8 moulds (die-casting moulds or injection moulds) manufactured per person per year, which is higher than that of many other countries. The service life of the moulds is long; the die-casting mould for sewing machine bodies produced by Switzerland's Bühler Group once achieved a service life of 70,000 to 80,000 cycles. The main equipment used for manufacturing moulds in Switzerland is CNC machine tools. Notably, Swiss companies once accounted for 40% of the world's top 10 mould manufacturers in terms of number. **Major Swiss Mould Manufacturers**: 1. **SCHTTLI**: SCHTTLI is a global Swiss mould manufacturing enterprise specializing in the R&D and production of high-precision and high-efficiency moulds, with expertise in the MED (medical), CAP (caps and closures), and PAC (packaging) sectors. In 2013, Husky Injection Molding Systems completed the acquisition of SCHTTLI. SCHTTLI has long focused on the development and manufacturing technology of moulds for medical applications, including syringes, infusion/blood transfusion products, and diagnostic systems. 2. **FOSTAG**: Swiss mould manufacturer FOSTAG is globally renowned for its thin-wall technology and blood collection tube technology. It has mastered specialized technical know-how in various in-mould labeling (IML) applications. The efficiency of FOSTAG moulds lies in their fast cycle times and long service life. 3. **KEBO**: Founded in 1979, KEBO still independently develops hot runners for its multi-cavity high-quality moulds. 80% of the company's business focuses on moulds for medical consumables and medical-related products, while 20% is dedicated to packaging moulds. Its core hot runner technology enables more compact mould design. The moulds delivered to clients include 128+128 stack moulds and 192-cavity moulds. Its modular design allows for flexible replacement of spare parts, with 100% interchangeability of mould and hot runner components. 4. **TANNER**: TANNER is a global leader in pipette tip moulds. Automation equipment manufacturer HEKUMA adopts TANNER's 4/6/8 series modules. TANNER's high-performance injection moulds are used for producing high-quality plastic products worldwide, holding a prominent position in terms of precision, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Its 64-cavity hot runner injection mould for 1000ul pipette tips utilizes side gating technology with a molding cycle of approximately 5 seconds. The unique 4/6/8 series modules feature a very compact mould structure for easy operation. Each cavity module is embedded with gating components, and the entire module can be directly installed and removed on the parting surface. The modular design also achieves optimal cooling circuits. ## IX. Austria Austria is an important global powerhouse in mould manufacturing, with many of its mould enterprises boasting a very high level of manufacturing capabilities. Although Austrian mould factories have not yet achieved fully automated mould manufacturing, the entire mould manufacturing process in Austria uses unified reference fixtures, eliminating the need for manual calibration. Robots or manipulators are employed for some repetitive production tasks. High-end equipment is standard in Austrian mould workshops. In particular, the clean and bright workshop environment, as well as the craftsmanship confidence reflected in the workers' mental outlook, all demonstrate the high level of Austria's mould industry. Austria is home to world-leading mould enterprises. For example, Austria's K.T.W, one of the world's top 10 mould manufacturers, is a leading global manufacturer of bottle cap moulds. It was acquired by Husky in 2011. K.T.W moulds provide innovative technical solutions, including multi-component technology, in-mould assembly and in-mould closing, cube, single-sided or stack mould designs. Its unique EASYcube technology offers industry-leading reliability, flexibility, and compatibility with similar professional bottle cap products. ## X. France France is an industrially developed European country, and Europe is one of the most developed regions in the world's mould industry. The standard for injection moulds in France is the ROUBARDIN standard, and the well-known German HASCO standard is also adopted in France. As we all know, European moulds are characterized by high efficiency, precision, and long service life. In addition to mould design and maintenance, the most important factors determining the reliability of moulds include mould steel, heat treatment methods, and mould processing technology. A notable feature of French moulds is fully automated molding. For example, for moulds in specialized industries in France, hot runners (hot nozzles) are used for gating whenever possible, or submerged entry, banana (horn) gating is adopted. All sprues must be automatically cut and dropped. According to the size and structural characteristics of the products, French moulds adopt a 1-out-of-8 design, with submerged gates for side gating of the products, enabling automatic separation during mold opening. All moulds avoid the use of ordinary large sprues, which require manual post-processing to cut off the sprues to separate them from the products. This is because labor costs are high, manual cutting of sprues results in significant variations, cutting sprues with nippers or knives easily scratches the plastic parts, leading to defective products, and workers are also prone to injuries and fatigue. Therefore, manual cutting of sprues is inconsistent with the clients' requirements. France is home to world-leading mould manufacturers. For example, France's PLASTISUD is a global leading supplier of high-performance, high-precision, and high-cavity moulds, mainly providing clients with fast, high-performance, and high-cavity moulds for applications such as beverage bottle caps, medical components (e.g., petri dishes, actuators, and sprayers), and packaging fields (e.g., thin-walled containers and in-mould labeling applications). In the field of high-cavity bottle cap moulds, PLASTISUD is the only company capable of producing and commercially applying 144-cavity bottle cap moulds. Its 144-cavity 29/25 mineral water bottle cap mould in operation at client factories has a molding cycle of only 2.8 seconds, with a production capacity of approximately 3,000 bottle caps per minute. For the 144-cavity mould used in CSD (carbonated soft drink) applications to produce 2.8g 1810 bottle caps, the cycle time is only 4.5 seconds, with a production capacity of 1,920 bottle caps per minute.
 中文
中文 English
English